One central philosophy guided my years of American history instruction. The story had to feel personal to each student, after all it is their country. For the unit on World War Two, I aimed to act as a bridge between my grandparents generation to the kids seated before me. While growing up, my grandparents played a large part in shaping my world view, as the old folks often shared their life experiences. Each had a unique tale on how they committed to fight totalitarianism abroad in the 1940’s, and defend democracy at home.
All the following accounts involved inconvenience, sacrifice, and interruptions to family life. At that singular moment all they knew was to serve their country, and defeat foreign tyranny.
A new dark age lay in America’s defeat.
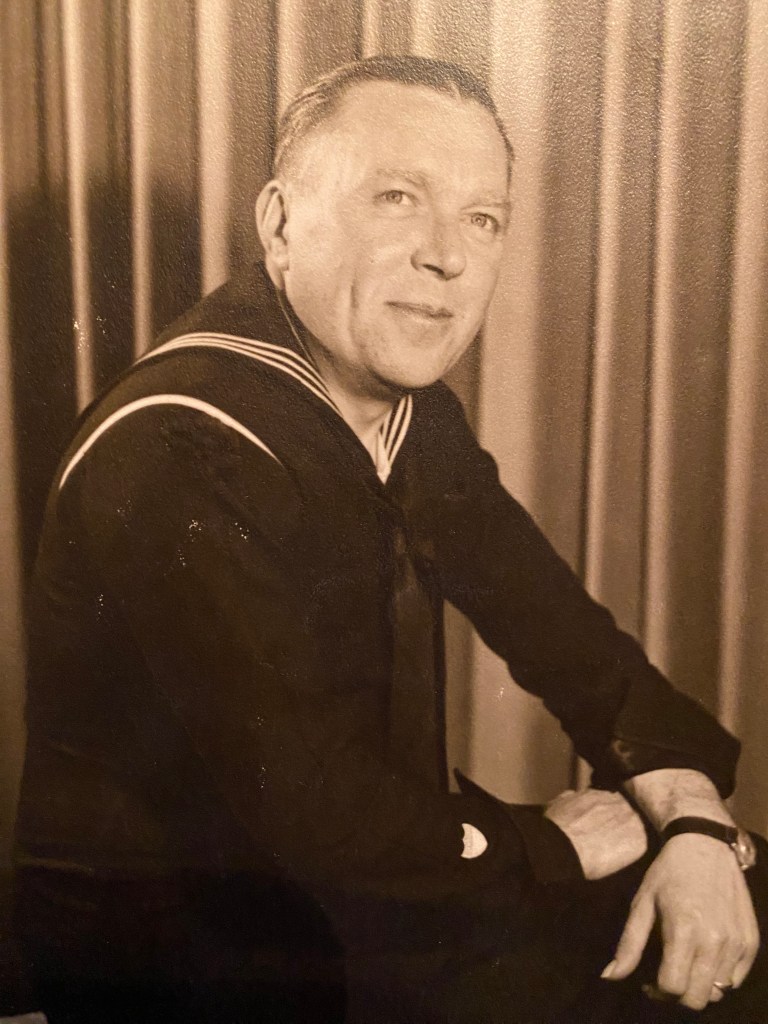
This is Ray Turner, born in 1905 in Hammond, Illinois. This young man migrated west, joining family members in Northern Idaho. Ray soon found his way to Spokane, Washington, where he found work as a postal carrier. Stopping for lunch along his mail route he met a waitress in a downtown cafe, Ailene Peterson, a single mother of one, and after a while they fell in love. Marrying in the fall of 1941, the newly weds, while on a Sunday drive caught a breaking news bulletin on the car radio that the Japanese had attack on Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. Ray turned his automobile around, motored back to Spokane, and joined the Coast Guard the next morning. Stationed out of Willapa Bay in Tokeland, Washington, Ray and the crew of the USS Manzanita patrolled the extensive, rugged Pacific coastline of Washington and Oregon monitoring for Japanese vessels. And it was aboard the Manzanita that Ray remained until August,1945 when he mustered out of the service and returned to Spokane. After a life of grandkids, holidays, and fun on his lake property, he retired from the US Postal Service, passing away in 1974.
Kurtz Olson hailed from Wing River, Minnesota, born on a frigid day in January, 1905. Kurtz, as the youngest of seven children took up welding as a young man, and made a fair living during the difficult Depression years. This photo, take in the 1930’s, (Kurtz on the left) indicates that Hitler was considered harmless and laughable. That certainly changed in 1939, and after the Pearl Harbor attack brought America into the war, Kurtz packed up his wife and family and traveled west to Tacoma, Washington in search of war work. Kurtz spent his days dismantling scrap metal in a welding yard preparing the steel for conversion to ships, planes, tanks, and other war materiel. After the war Kurtz moved his family to Spokane, where he welded, owned a series of mutts, cut firewood with his son, and grandson’s. Kurtz passed on in 1989.

This GI is Joe Tucker, this snapshot taken somewhere in France around 1944. Born in Craig County, Oklahoma in 1907, Joe found himself back in uniform at the ripe old age of 37, much older than the 18 and 19 year-olds in his outfit. Joe had actually been in the army until 1939, receiving his first discharge before the war. Making his way to the Pacific Northwest he too, settled in Spokane where he met and married a widow with three children. His daughter from his first marriage lived in the city, as well, and he wanted to remain near her. Working for the Northern Pacific Railroad, with his new, larger family, Joe joined the Washington National Guard for the extra pay guard duty brought in. After Pearl Harbor the US Government nationalized the Washington Guard, and off he went to war. After training stateside, then stationed in the south of England, Joe found himself on Normandy Beach on June 7, 1944, D+1. Surviving those first days he and his fellow Guardsmen suffered through the Battle of the Bulge, finally winding their way to Germany. On one particular night, Joe stood guard duty somewhere in Germany. He heard his sergeant grouse was the soldier on duty asleep? The reply was no, it’s Tucker, and he’s awake alright. (Joe liked telling that story). Eventually Joe shipped home to reunite with his family in 1945.
From her waitressing job, Ailene Peterson, turned Ailene Turner followed her new husband Ray to the Washington coast. Traveling with her young daughter Ailene looked for war work as well. Born in 1914, in Clinton, Minnesota, Ailene had married quite young, desperate to leave her father’s stump farm in North Dakota. Husband #1, Joe Tucker had failed her, and with her young daughter in tow, sought refuge with family members in Spokane. It was in Bremerton, Washington that she found employment wiring mine sweepers for America’s Russian allies, (she said they were very rude). In later life, Ailene proudly mentioned that her work never had to be redone. She always wired it right the first time. In an operators cab of a crane, Ailene noticed the girls below waving their arms and jumping about. Shutting down the motor she heard them yell that the Japanese had surrendered, and the war was over. Ailene scrambled down from her seat, and joined the victory celebration. She, too, along with Ray returned to Spokane until her death in 1990.
Besides being my grandparent’s, and generously sharing their remarkable stories with me, what else did these people share in common? They put aside their personal lives to step up in defiance of fascism and authoritarianism. They knew that service to America, to our democracy, was their first duty.
Retelling my grandparent’s war-time sacrifices to my history students added a vividness to the coursework that encouraged the kids to do the same with their elders. That, once again is how I bridged the war years to now, making it personal for students.
President Roosevelt had characterized that moment as America’s “Rendezvous with Destiny,” and those people rose masterfully to the challenge. And despite all the hostility to democracy today, we cannot surrender to those forces, and betray our forebears who stood up to defend our way of life.
Perhaps now is our “Rendezvous with Destiny,” and this time all we have to do is vote for the Democrat over the wannabe dictator.
Once again, a new dark age lay in America’s defeat.
Gail Chumbley is the author of the two-part memoir, “River of January,” and “River of January: Figure Eight.” Both are available on Kindle. Chumbley has also penned two history stage plays, “Clay,” and “Wolf By The Ears.” She is the co-author of “Dancing On Air,” and feature length screenplay, and is working on “Peer Review,” for the stage, a series of short plays where DJT meets real presidents from the past.
gailchumbley@gmail.com